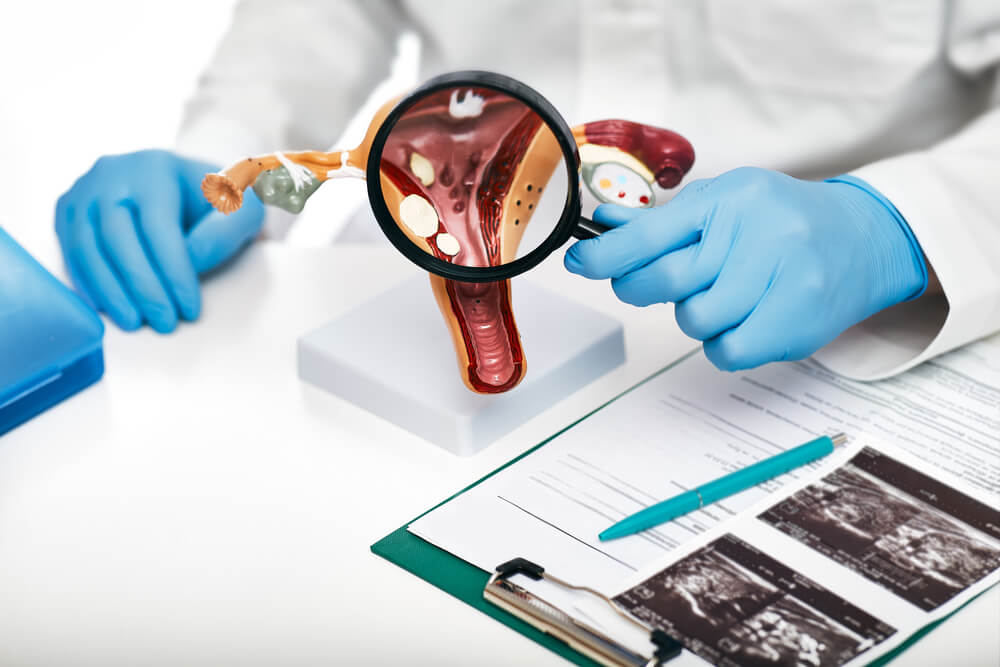
Uncover the expert-approved facts about uterine polyps and educate yourself today. This article outlines and explains the common causes, symptoms, and treatment methods available to patients dealing with uterine polyps. If left undiagnosed and untreated, uterine polyps can cause issues with fertility and menstruation.
If you or a loved one received a diagnosis for this condition, you may feel concerned and maybe even frightened. Firstly, it is essential to seek out the advice and guidance of a trained professional at a reliable clinic. If you are in the area or you are looking for the best, we recommend consulting with gynecology specialists in Miami.
With that in mind, here is everything you should know about uterine polyps.
What is the Definition of Uterine Polyps?
In the simplest terms, the growths that appear in the endometrium or the inner lining of the uterus are called uterine polyps. These polyps are attached to the uterus’s inner lining by a broad base or thin stalk. Uterine polyps extend inward into the patient’s uterus. While polyps are typically noncancerous, they can cause challenges with fertility and can cause irregular bleeding. Often, polyps are oval or round and can be of different sizes, ranging from a couple of millimeters to a couple of centimeters (or bigger). Some patients have several or only one uterine polyp.
To maximize your health and ensure optimal fertility levels, we recommend seeking out the help of trained professionals at New Age Women’s Health. Get the treatment you deserve and maximize your health.
Who Can Get Uterine Polyps?

One of the most significant risk factors for uterine polyps is advanced age. Patients who are in their 40s and 50s have a higher chance of dealing with polyps, as this is the time of perimenopause. Polyps can also occur in patients in their 20s and 30s but this is less often.
Risk factors for polyps include:
- BMI (body mass index) over 25
- Hypertension or high blood pressure
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Use of tamoxifen, a breast cancer treatment drug.
Research also reveals that some populations are at greater risk of polyps. For example, women who have gone through menopause have a higher chance of polyps than women in perimenopause or those who are younger than 20.
It is also interesting to note that postmenopausal women have a slightly higher chance of malignant cervical polyps. The same is true for women in perimenopause.
What are the Common Symptoms of Uterine Polyps?
As mentioned, polyps can be asymptomatic, so you might not experience any symptoms. However, there are some signs to look out for. One of the most common symptoms of uterine polyps is unusual bleeding, including irregular menstrual periods and vaginal bleeding following menopause. A lot of patients dealing with uterine polyps experience irregular menstruation.
Other symptoms may include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Irregular menstrual cycles (unusual flow and timing).
- Spotting or bleeding between menstrual cycles or intermenstrual bleeding.
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse.
- Infertility problems (inability to carry a pregnancy or conceive a baby).
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting following menopause (brown, pink, or red-colored blood).
In some situations, polyps may be located in the cervix. When this happens, the healthcare professional may notice the polyp during a regular physical examination and pap smear.
While all of the above symptoms can be seen with uterine polyps, some of these same signs are also seen with uterine cancer. Therefore, you should see your doctor immediately if you experience any of these symptoms, as further workup should occur.
If you believe you may have uterine polyps and cancer symptoms, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional immediately. Talk honestly with your doctor about what you are experiencing. Your healthcare provider will give you a proper diagnosis and help you with further treatment. Do not stall your appointments. Contact your doctor today and find out the cause of your symptoms.
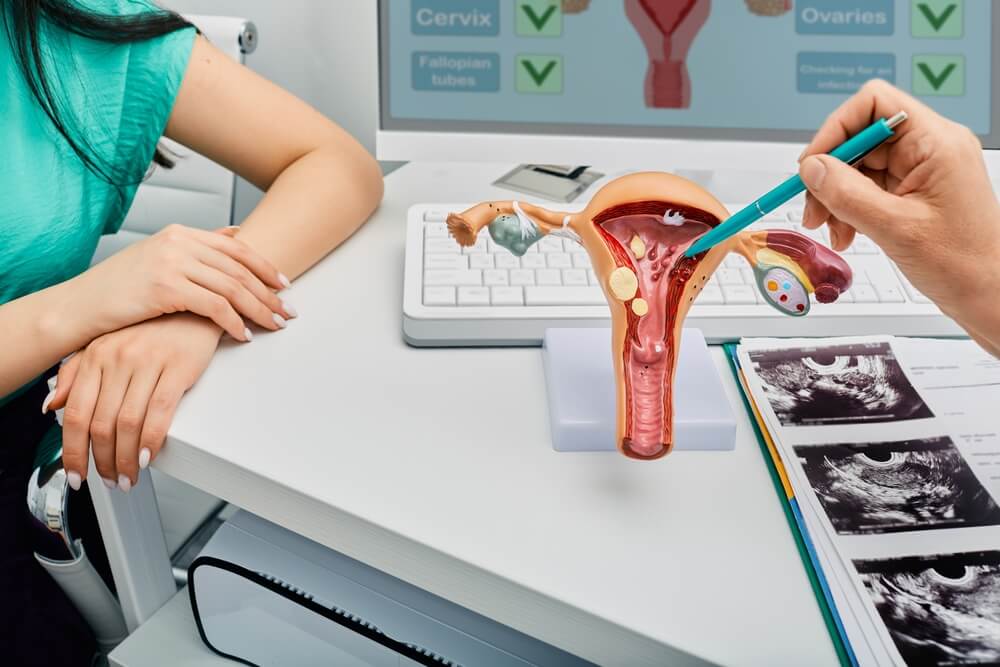
Diagnosing Uterine Polyps: What You Need to Know
Your doctor will review your medical history and inquire about the symptoms you may be experiencing. They may ask you about medications you are taking or if you notice spotting or bleeding. The doctor will also perform a thorough gynecological exam, including a pelvic exam. Some additional tests may be required, such as:
- A transvaginal ultrasound: This is the best way to take pictures of the uterus and ovaries. The lining of the uterus, in particular, will be measured and assessed for the presence of a polyp.
- Sonohysterogram: This is a specialized type of ultrasound during which fluid is placed inside of the uterus to visualize better what is inside the lining. While this test is not always performed, it is often recommended after a transvaginal ultrasound if a polyp is suspected but not clearly seen.
- Hysteroscopy: If a uterine polyp is identified, your doctor will likely recommend removal. A hysteroscopy is a procedure in which a camera is placed inside of the uterus. Specialized instruments can also be used at this time to remove the polyp. This procedure can be done in an office or an outpatient surgery center.
- Endometrial biopsy: This procedure occurs in an office and involves collecting a sample of tissue from the lining of the uterus. While this procedure is not necessary once a polyp has been discovered, it may be needed if your doctor suspects a precancer or cancer inside the uterus after a transvaginal ultrasound is performed.
How Do You Treat Uterine Polyps?
Uterine polyps are treated by having them removed. The most common procedure to remove polyps is a hysteroscopy. This procedure involves having a camera placed inside the uterus and a special instrument is used to remove it. Luckily, this procedure is overall considered very safe and does not take a long time. The procedure can also be performed in a doctor’s office under local anesthesia or in an outpatient surgery center.
Are There Ways to Prevent Polyps?
Sadly, there is no way to prevent polyps. However, you can receive early diagnosis and treatment. This way, you can avoid uncomfortable symptoms and future complications.
What are the Chances that the Polyps in the Uterus are Cancerous?
Just five percent or less of polyps in the uterus are cancerous. If you have any further doubts or concerns, talk to a medical professional for expert advice.
When Should I Get Treated?
You should schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider if you are experiencing:
- Unpredictable or heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Spotting or vaginal bleeding when you don’t have your period.
- Spotting or vaginal bleeding following menopause.
Give Us a Call Today
Take care of your health today and reach out to our friendly and compassionate team of medical experts. Give us a call today to get started with your healing journey.