Getting your tubes tied is an expression you have probably heard before. This means that your ability to get pregnant is permanently stopped. People most often decide to get tubal ligation when they do not want to have any more children and do not wish to deal with different birth control methods.
In order to get proper advice and guidance when deciding whether to have tubal ligation surgery, you have to choose experienced, knowledgeable specialists who will help you map out the benefits and the risks. My OBGYN Specialists clinic offers continuous counseling and helps patients who decide to tie their tubes, so make sure you check them out!
Tubal Ligation 101
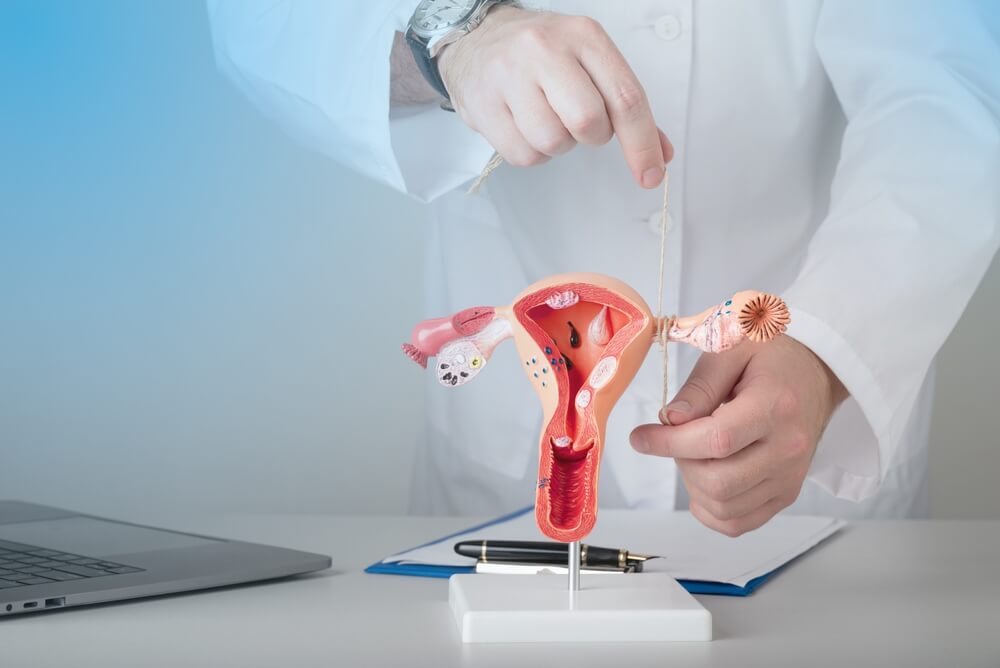
As mentioned, tubal sterilization, female sterilization, or tubal ligation is a surgery that serves as permanent birth control. During the procedure, the fallopian tubes are blocked, tied, or cut to permanently stop them from enabling future pregnancies. Preventing the egg from traveling toward the uterine lining through the fallopian tubes is the main task when it comes to this procedure. That said, it is important to emphasize that this surgery does not affect your menstrual cycle, so you can expect to continue getting your period as usual.
To clarify in more detail the role of the fallopian tubes, it is essential to explain the impregnation process as well. The reproductive system is formed by four organs: the uterus, vagina, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. When an egg is released from the ovaries, the fallopian tubes are used as a transportation pathway toward the uterus, where the pregnancy will officially begin. When the tubes are closed, the sperm can’t get to the egg anymore, and this logic is used when it comes to tubal ligation surgery.
It can be done at any point in time, and sometimes doctors combine it with other procedures, such as a C-section. This procedure cannot be reversed in most cases, and if you want to get a reversal, it will require major surgery, which might not be effective whatsoever.

The Why?
Considering that tubal ligation is 99% effective in pregnancy prevention and is a very safe procedure, people decide to undergo this process to practice and enjoy sexual relations without having to worry about pregnancy. Additionally, removing fallopian tubes is sometimes recommended as a treatment for certain conditions or when there is a risk for you to be a carrier of a gene mutation causing ovarian cancer.
Be aware that permanent birth control does not protect the person from sexually transmitted infections and diseases, so you need to take care of your reproductive health even though you have undergone tubal ligation.
Deciding to undergo such a procedure demands careful consideration and consultations with your chosen medical provider. Reversal of this kind of intervention is very risky, and you might not get positive results, so make sure you deliberate on all the risks, benefits, and complications before you make your final decision.
Preparation for Surgery
Your chosen healthcare provider needs to give you all the necessary recommendations to help you prepare to the best of your abilities. You should discuss with them all potential risk factors and details of the procedure, so you can also mentally prepare and plan your recovery.
There are no particular preparatory steps before the surgery, although some experts recommend using contraception at least one month prior to the surgery. Also, before the surgery begins, you might need to take a pregnancy test so the doctors know for sure you are not pregnant.
Tubal Ligation Surgery Procedure
This procedure can be done in three ways, and they include:
- Laparoscopic tubal ligation: This approach is done through two tiny incisions, one on the navel and the other above the pubic bone. Using a laparoscope, the doctor seals the fallopian tubes with a clip, ring, or band. Sometimes an electric current is also used to seal the tubes. This type of tubal ligation can be done whenever, and the small incisions reduce the recovery time and the potential risks.
- Laparotomy: A more extreme approach to tying your tubes, where a very big incision is made on the abdomen, and through that incision the doctor brings up the fallopian tubes in order to close them off with clamps, rings, or bands. It takes a few days to recover from the procedure in the hospital and a few weeks to continue the recovery at home. This is quite an outdated procedure.
- Mini-laparotomy tubal ligation or mini-lap is usually done within a day from the vaginal delivery of the baby while the patient is still under epidural or spinal anesthesia. The incision is much smaller, although the procedure is quite similar to a laparotomy.
Recovery
Most often, patients are free to go home a few hours after tubal ligation, especially if it’s done laparoscopically. There might be a slight discomfort around the incision, and you might experience pain in the abdomen, nausea, dizziness, exhaustion, shoulder pain, and bloating. If any pain occurs after the procedure, you can take some over-the-counter painkillers. If this continues, please get in touch with your chosen doctor.
Do not rub the incision, consume alcohol or bathe at least two days after the surgery. Also, avoid lifting anything heavy or engaging in sexual intercourse at least one week post-op. If symptoms such as fainting, high fever, severe pain in the abdomen, vaginal discharge, or bleeding occur, call your doctor and let them know.
Eat light meals such as soups, crackers, or toast to help you with any potential nausea, and do not be alarmed if you start experiencing light vaginal bleeding because that is completely normal at least one month after the surgery. The menstrual cycle might not normalize for a month or two after the procedure but do not worry too much; just speak to your doctor and let them guide you through the recovery process.
Tubal Ligation Side Effects
Several tubal ligation side effects might occur after the surgery, and they include:
- Pain in the abdomen
- Feeling tired
- Anesthesia side effects
- Shoulder pains
- Sore throat
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Cramping
- Bloating
- Pelvic pain

Benefits and Risks
Aside from being a permanent solution, tubal ligation has very few risks considered severe and dangerous. The benefits outweigh the risks in the case of tying your tubes, and they can include the following:
- The procedure is highly effective
- Convenience
- Reduction of risk of cancer and other conditions
- Non-hormonal option for birth control
One of the most critical risks to consider is regret because some studies show that around 12% of those who choose to be sterilized regret the decision and want to reverse it. It is recommended to wait until you are of a certain age and carefully consider all offered options.
Speak to Our Experts!
The topic of tubal ligation has been present for quite some time now, and our experts are here to answer all your potential questions and support you if you decide to undergo this procedure. Pick up the phone and call us today!